Benefits of Open Source Technology
Open source software (OSS) has become increasingly popular in recent years, with businesses of all sizes adopting it for a variety of reasons. Here are some of the key benefits of companies adopting open source software:
- Cost savings: OSS is often free or very low-cost, which can save businesses a significant amount of money on software licenses. This is especially beneficial for small businesses, which often have limited budgets.
- Flexibility: OSS is typically very flexible and can be customized to meet the specific needs of a business. This can be a major advantage, as it allows businesses to avoid being locked into a particular software solution.
- Scalability: OSS is often scalable, which means that it can grow with a business as it needs to add more users or features. This can be a major benefit for businesses that are experiencing rapid growth.
- Security: OSS is often very secure, as it is constantly being reviewed and updated by a large community of developers. This can be a major advantage for businesses that are concerned about security.
- Innovation: OSS is often more innovative than proprietary software, as it is developed by a large community of developers who are constantly working to improve the software. This can be a major benefit for businesses that are looking for the latest and greatest technology.
In addition to these benefits, OSS can also help businesses improve their reputation and attract top talent. When businesses use OSS, they are seen as being innovative and forward-thinking. This can help them attract new customers and employees.
Overall, there are many benefits to companies adopting open source software. If you are considering adopting OSS, be sure to weigh the benefits and drawbacks carefully to make sure that it is the right decision for your business.
Here are some additional benefits of using open source software for businesses:
- Increased collaboration: OSS is typically developed and maintained by a large community of developers. This can lead to increased collaboration between businesses and developers, as businesses can provide feedback and suggestions to help improve the software.
- Improved transparency: OSS is typically open-source, which means that the source code is available for anyone to view. This can lead to improved transparency, as businesses can see how the software works and make sure that it is secure and reliable.
- Reduced risk: OSS is typically well-tested and has a long track record of use. This can reduce the risk of businesses experiencing problems with the software.
If you are looking for a cost-effective, flexible, scalable, secure, innovative, and collaborative software solution, then open source software is a great option.
Linux Based Services
We design our services using Linux to provide a structured, standardized approach to the installation and configuration of the CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian or Red Hat Linux Server or any other suitable distribution of Linux operating system.
Linux is an open platform that can be the foundation for almost anything your business needs. Here are some examples of how businesses can use Linux and open source software to build their infrastructure:
- Web servers: Linux is a popular choice for web servers because it is stable, secure, and scalable. Popular web server software such as Apache and Nginx are available for Linux.
- Database servers: Linux is also a popular choice for database servers because it is reliable and efficient. Popular database software such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB are available for Linux.
- File servers: Linux is a good choice for file servers because it is secure and easy to manage. Popular file server software such as Samba and NFS are available for Linux.
- Email servers: Linux is a popular choice for email servers because it is reliable and secure. Popular email server software such as Postfix and Exim are available for Linux.
- Virtualization: Linux is a popular platform for virtualization because it is stable and scalable. Popular virtualization software such as VMware, VirtualBox, and KVM are available for Linux.
- Domain controllers: Linux based domain controlls allow your company to authenticate and validate Windows desktop users on a network, including group policies, user credentials, and computer names to determine and validate user access. By using a Linux-based domain controller, businesses can reduce their dependency on Microsoft. This can be beneficial for businesses that are looking to reduce their costs or that are concerned about vendor lock-in while having more control over their IT infrastructure. This is because Linux is an open-source operating system, which means that businesses can choose the hardware, software, and configuration that best meets their needs.
- Database servers: Open source databases are freely available to anyone to use, modify, and distribute.
Some examples of popular open source databases used on an Enterprise level:- MySQL: MySQL is a popular relational database management system (RDBMS) that is known for its speed, reliability, and ease of use. It is used by a wide variety of businesses, including small businesses, large enterprises, and government agencies.
- PostgreSQL: PostgreSQL is a popular open source object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) that is known for its scalability, performance, and flexibility. It is used by a wide variety of businesses, including small businesses, large enterprises, and government agencies.
- MongoDB: MongoDB is a popular NoSQL database that is known for its flexibility and scalability. It is used by a wide variety of businesses, including startups, small businesses, and large enterprises.
- Cassandra: Cassandra is another popular NoSQL database that is known for its scalability and high availability. It is used by a wide variety of businesses, including startups, small businesses, and large enterprises.
- Phone systems and telephony applications: Your business can get all of the features and reliability you expect without the per-phone, per-port, and per-feature price increases typically found with other systems.

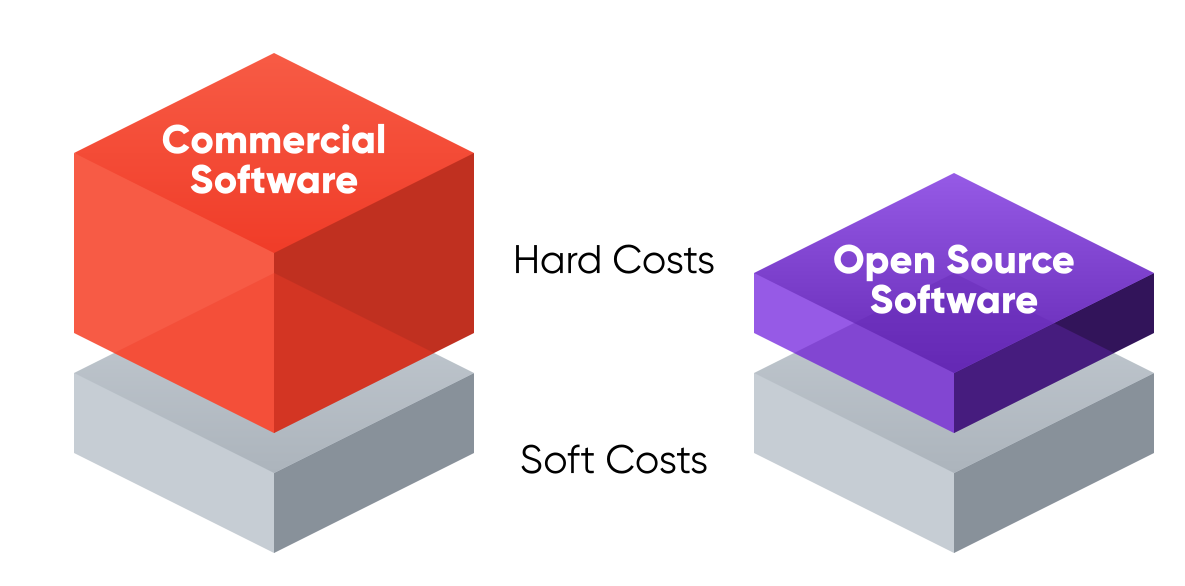
If the software is free...what are you paying for?
When companies implement open source software, they may pay for the following:
- Support: There are many companies that offer support for open source software. This support can include things like:
- Answering questions about how to use the software
- Providing bug fixes and security updates
- Helping to troubleshoot problems
- Training: There are many companies that offer training on how to use open source software. This training can be helpful for businesses that want to get the most out of the software.
- Customization: Open source software can often be customized to meet the specific needs of a business. This customization can be done by the business itself or by a third-party vendor.
- Hardware: Open source software can run on a variety of hardware platforms. However, some businesses may choose to purchase hardware that is specifically designed for open source software. This hardware can offer better performance and/or security than general-purpose hardware.
In addition to these direct costs, companies may also incur indirect costs associated with implementing open source software. These indirect costs can include:
- Staff time: Implementing open source software can require staff time to:
- Evaluate the software
- Install the software
- Configure the software
- Train employees on how to use the software
- Lost productivity: Implementing open source software, like all software, can sometimes disrupt business operations unless planning occurs to prevent business disruptions and productivity loss.
Overall, the cost of implementing open source software varies depending on the specific needs of the business. However, the costs associated with open source software are often significantly lower than the costs associated with proprietary software.